1. Ultimate Guide To Designing Your Special Ed Mastery Plan

Introduction to Designing Your Special Ed Mastery Plan

Designing an effective Special Education Mastery Plan is crucial for ensuring that students with diverse learning needs receive the support and accommodations they require to thrive academically and socially. This comprehensive guide aims to provide educators, administrators, and special education professionals with a roadmap to create personalized and inclusive learning environments. By following these steps, you can empower students with special needs to reach their full potential.
Understanding Special Education Needs

Before diving into the mastery plan, it’s essential to grasp the unique challenges and strengths of students with special education needs. These students may have varying disabilities, such as learning disabilities, intellectual disabilities, autism spectrum disorder, or physical disabilities, each requiring tailored approaches. Understanding these diverse needs is the foundation for creating an effective mastery plan.
Conducting Comprehensive Assessments

Comprehensive assessments are the cornerstone of an effective Special Education Mastery Plan. These assessments should go beyond academic performance and include social, emotional, and behavioral evaluations. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify Assessment Goals: Determine the specific areas you want to evaluate, such as reading comprehension, math skills, social interaction, or fine motor skills.
- Select Appropriate Assessment Tools: Choose standardized tests, observational checklists, or interviews that align with your assessment goals. Ensure the tools are valid and reliable.
- Administer Assessments: Conduct assessments in a comfortable and familiar environment. Provide accommodations if necessary to ensure accurate results.
- Analyze Results: Interpret the assessment data to identify the student’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas requiring intervention. Look for patterns and trends.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Involve parents, caregivers, and other professionals (e.g., speech therapists, occupational therapists) in the assessment process to gain a holistic understanding of the student’s needs.
Developing Individualized Education Plans (IEPs)

Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) are tailored roadmaps for each student with special needs. They outline the specific goals, accommodations, and services required to support their learning journey. Here’s how to develop effective IEPs:
- Set Meaningful Goals: Define measurable and achievable goals based on the assessment results. Ensure goals are specific, realistic, and aligned with the student’s strengths and interests.
- Determine Accommodations: Identify the necessary accommodations and modifications to support the student’s learning. This may include extended time for tests, alternative assessment formats, or assistive technology.
- Select Appropriate Services: Collaborate with special education professionals to determine the most suitable services, such as specialized instruction, speech therapy, or occupational therapy.
- Involve the Student: Engage the student in the IEP development process whenever possible. Their input and participation can enhance motivation and ownership.
- Regularly Review and Update: IEPs should be living documents, reviewed and updated regularly to reflect the student’s progress and changing needs.
Creating Inclusive Learning Environments

An inclusive learning environment is crucial for the success of students with special needs. Here are some strategies to foster inclusivity:
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL): Implement UDL principles to create flexible and accessible learning experiences. This includes offering multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression.
- Peer Support: Encourage peer interaction and collaboration. Peer support can enhance social skills, promote inclusivity, and provide a sense of belonging.
- Sensory-Friendly Spaces: Design sensory-friendly areas within the classroom or school to accommodate students with sensory processing challenges.
- Visual Supports: Utilize visual aids, graphic organizers, and visual schedules to support understanding and organization.
- Positive Behavior Supports: Implement positive behavior intervention strategies to promote appropriate behavior and social skills.
Implementing Accommodations and Modifications

Accommodations and modifications are essential tools to ensure students with special needs can access the curriculum and demonstrate their learning. Here’s how to implement them effectively:
- Teacher Training: Provide professional development opportunities for teachers to understand and implement accommodations effectively.
- Assistive Technology: Explore and utilize assistive technology tools such as text-to-speech software, voice recognition software, or specialized keyboards.
- Alternative Assessment Methods: Offer alternative assessment formats, such as oral presentations, projects, or portfolios, to accommodate different learning styles.
- Flexible Scheduling: Consider flexible scheduling options to accommodate students’ needs, such as extended time for tests or breaks during extended periods of learning.
- Individualized Instruction: Differentiate instruction to meet the unique needs of each student, providing additional support or challenges as required.
Monitoring and Evaluating Progress
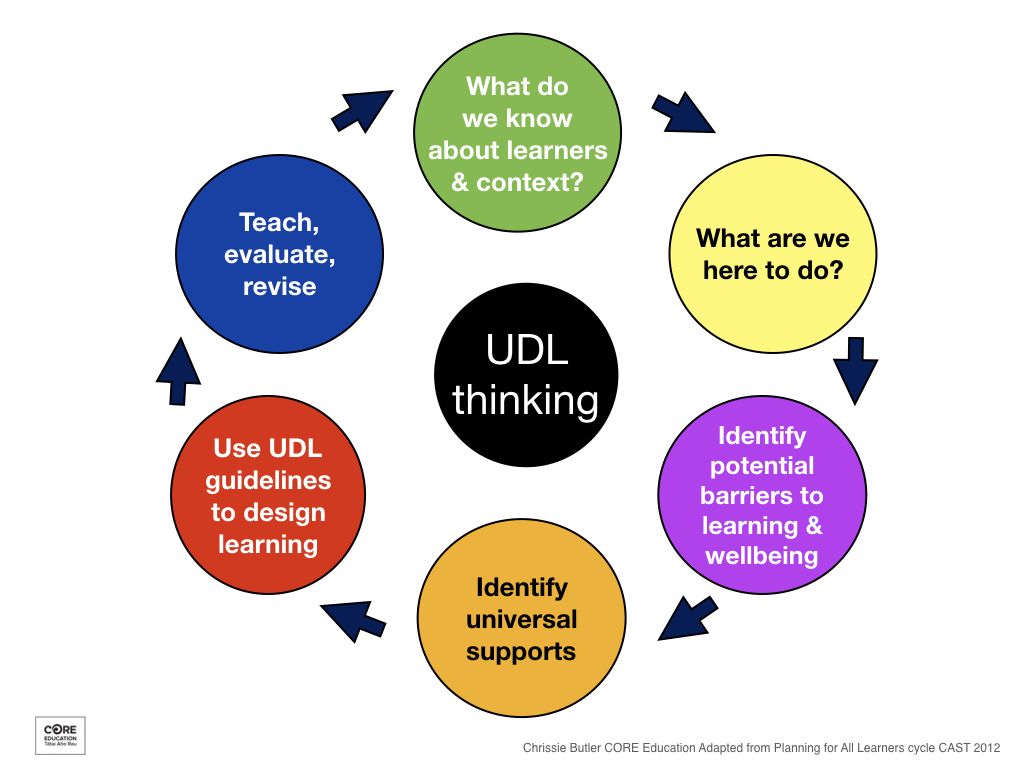
Regular monitoring and evaluation are vital to ensure the Special Education Mastery Plan is effective and aligned with the student’s progress. Here’s how to approach this:
- Establish Progress Monitoring Systems: Implement systems to track the student’s progress towards IEP goals. This may include regular check-ins, progress reports, or data collection.
- Analyze Data: Regularly review and analyze progress data to identify areas of improvement or success. Use data-driven decision-making to adjust the plan as needed.
- Collaborative Problem-Solving: Engage in collaborative problem-solving with the student’s IEP team to address any challenges or setbacks.
- Share Progress with Stakeholders: Keep parents, caregivers, and other professionals informed about the student’s progress and involve them in decision-making.
Building a Supportive Community

Creating a supportive community is essential for the well-being and success of students with special needs. Here are some strategies to foster a supportive environment:
- Teacher Collaboration: Encourage collaboration among teachers to share best practices and support each other in implementing the mastery plan.
- Parent Engagement: Involve parents and caregivers in the educational process. Provide resources and support to help them understand their child’s needs and how they can assist at home.
- Community Partnerships: Collaborate with local organizations, such as disability support groups or community centers, to provide additional resources and support.
- Professional Development: Offer ongoing professional development opportunities for special education professionals to stay updated on best practices and emerging research.
Embracing Cultural and Linguistic Diversity

In today’s diverse society, it’s crucial to consider the cultural and linguistic backgrounds of students with special needs. Here’s how to address this:
- Cultural Competence: Ensure teachers and staff receive training on cultural competence to understand and respect diverse cultural backgrounds.
- Language Access: Provide language support services, such as bilingual education or translation services, to accommodate students with limited English proficiency.
- Inclusive Curriculum: Review and adapt curriculum materials to ensure they are culturally relevant and inclusive of diverse perspectives.
- Family Engagement: Involve families from diverse backgrounds in decision-making processes and provide resources in their native languages when possible.
Transition Planning

Transition planning is a critical aspect of the Special Education Mastery Plan, especially as students approach graduation or significant transitions. Here’s how to approach it:
- Start Early: Begin transition planning well in advance, ideally several years before the anticipated transition.
- Explore Post-Secondary Options: Help students explore post-secondary education, career, and independent living options that align with their interests and goals.
- Develop Transition Goals: Work with the student to develop specific transition goals, such as acquiring independent living skills or vocational training.
- Collaborate with Community Agencies: Partner with community agencies, such as vocational rehabilitation services or disability support organizations, to provide additional support and resources.
- Self-Advocacy Skills: Teach students self-advocacy skills to empower them to communicate their needs and rights as they transition into adulthood.
Notes:
- Assessment Tools: Ensure the assessment tools you choose are culturally sensitive and appropriate for the student’s age and ability level.
- IEP Collaboration: Involving the student and their family in the IEP process is crucial for buy-in and motivation.
- Inclusive Technology: Explore inclusive technology solutions to support students with special needs, such as screen readers or adaptive keyboards.
- Flexibility: Be prepared to adapt and adjust the mastery plan as the student’s needs evolve over time.
- Professional Development: Stay updated on the latest research and best practices in special education through ongoing professional development.
Conclusion: Empowering Students with Special Needs
Designing an effective Special Education Mastery Plan is a collaborative and ongoing process. By understanding the unique needs of students with special needs, conducting comprehensive assessments, and developing individualized plans, educators can create inclusive learning environments that empower students to reach their full potential. Remember, each student is unique, and their mastery plan should reflect their strengths, interests, and goals. With a well-designed plan and a supportive community, students with special needs can thrive academically, socially, and emotionally.
FAQ
How often should IEP goals be reviewed and updated?

+
IEP goals should be reviewed and updated at least once a year during the annual IEP meeting. However, if significant progress or setbacks occur, it’s important to convene additional meetings to adjust the goals as needed.
What are some common accommodations for students with special needs?

+
Common accommodations include extended time for tests, alternative test formats, preferential seating, use of assistive technology, and access to a quiet testing environment. These accommodations aim to level the playing field for students with special needs.
How can I involve parents in the IEP process effectively?

+
Effective parent involvement includes regular communication, providing resources and information about the IEP process, and inviting parents to participate in IEP meetings. Their insights and involvement are valuable in creating a successful plan.
What are some strategies for promoting positive behavior in students with special needs?
+
Positive behavior strategies include using visual schedules, providing clear expectations and rules, offering positive reinforcement for desired behaviors, and implementing behavior contracts or plans. Consistency and positive reinforcement are key.
How can assistive technology benefit students with special needs?

+
Assistive technology can enhance access to learning by providing alternative methods of communication, reading, writing, and organization. It can improve independence, engagement, and overall academic performance for students with special needs.



